SMDs Understanding: What Does SMD Mean?
Discover the meaning of SMDs with DXM, your trusted source for electronic components. Unravel the question, "What does SMD mean?" and explore the significance of Surface-Mount Devices in modern technology. As industry leaders, we provide insights into how SMDs enhance electronic product efficiency and design. Stay informed with DXM and elevate your tech understanding.
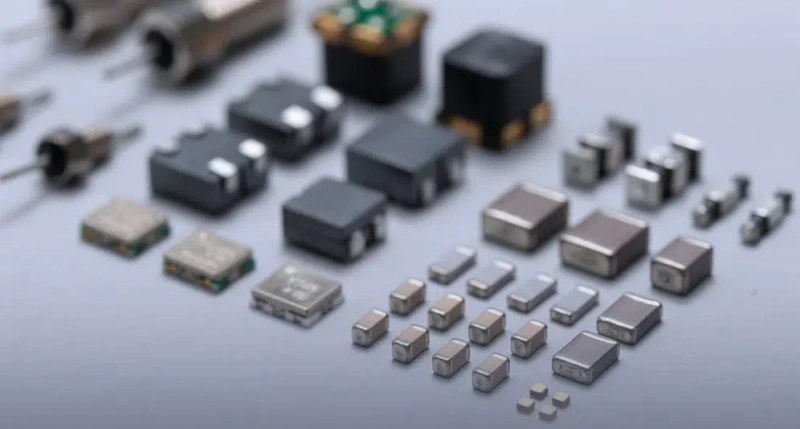
Have you ever wondered, "What does SMD mean?" You're not alone. The term SMDs refers to Surface-Mount Devices, which are crucial components in nearly all modern electronic devices. From your smartphone to your car's electronics, SMDs play a vital role. This article will explore what SMDs are, their evolution, benefits, applications, and how to choose the right SMD for your projects. Whether you're a professional in the electronics field or just curious about the technology behind your gadgets, this guide will answer your questions about what does SMD means.
What Does SMD Mean? The Basics
At its core, what does SMD mean? The acronym SMD stands for Surface-Mount Device. SMDs are electronic components that are attached directly to the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). This mounting process is different from traditional through-hole components, which require holes to be drilled in the PCB. Instead of passing through the PCB, SMDs are soldered directly to the board’s surface, allowing for more compact and efficient designs.
As electronics have become smaller and more powerful, SMD technology has evolved to meet these needs. The shift from through-hole to surface-mount technology (SMT) has enabled manufacturers to create devices with smaller footprints, faster processing speeds, and enhanced reliability. Understanding what does SMD means is key to grasping how modern electronic devices are built and why they perform better than their predecessors.
The Evolution of Surface-Mount Devices ( SMDs )
The transition to SMD technology was not instantaneous. Early electronic devices used through-hole components, which involved placing components through holes in the PCB. This method was effective, but it required a lot of space and manual labor, making it less efficient as technology advanced.
Over time, engineers recognized the need for a more compact, reliable, and automated solution. SMDs emerged as the perfect answer. By allowing components to be mounted directly on the surface of the PCB, SMDs enabled manufacturers to reduce the size of electronic devices while maintaining or even improving performance. This shift was crucial in the development of smaller, faster, and more reliable consumer electronics.
The evolution of SMDs also enabled the automation of the manufacturing process. Surface-mount technology allows machines to place components with high precision, leading to faster production times and fewer human errors. This shift from manual to automated assembly has revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry.
Key Benefits of SMDs in Electronics
Why are SMDs so widely used in modern electronics? The answer lies in their numerous advantages:
- Compact Size: SMD is much smaller than through-hole components, allowing for more compact device designs. This is particularly important in today’s world, where electronics are becoming increasingly miniaturized.
- Performance: SMDs offer superior electrical performance. With their reduced lead inductance, they provide faster signal transmission and are ideal for high-frequency applications.
- Automated Production: The small size and uniformity of SMDs make them perfect for automated assembly. This results in faster production and more consistent quality across large batches.
- Reliability: Because SMD does not have leads that go through the PCB, it is less prone to mechanical failure. This makes it more reliable, especially in environments where the devices will be subject to vibration or impact.
- Reduced Costs: The automation of the assembly process significantly reduces production costs, and because of their small size, SMDs also require less material, further driving down costs.
Common Applications of SMDs
SMDs are used in a wide range of electronic devices. From consumer electronics to industrial systems, these components are essential for making modern electronics more compact and efficient. Below are some of the most common applications of SMDs:
- Smartphones: The demand for smaller, thinner smartphones has driven the widespread use of SMD. These components allow manufacturers to pack more functionality into a smaller space.
- Computers and Laptops: SMDs are used in everything from motherboards to memory modules. Their compact size helps keep computers and laptops slim while maintaining high performance.
- Medical Devices: Many medical devices, such as pacemakers and diagnostic equipment, rely on SMD for its compact size and reliability.
- Automotive Electronics: Modern vehicles use a variety of electronic systems for everything from safety features to entertainment. SMDs are used in these systems to ensure they are both small and reliable.
- Consumer Electronics: Other consumer devices, including gaming consoles, TVs, and audio equipment, all use SMD to keep it compact and efficient.
How to Choose the Right SMD for Your Project
When designing an electronic device, choosing the right SMD is crucial. With so many different types available, it’s important to understand the specifications and requirements of your project. Here are some factors to consider when selecting SMD:
- Electrical Specifications: Ensure that the SMD can handle the voltage and current requirements of your device. Some SMDs are designed for high-power applications, while others are better suited for low-power circuits.
- Size Constraints: Depending on the design of your PCB, you may need a specific size of SMD. Choose an SMD that fits within your design specifications.
- Environmental Factors: Consider the operating environment of your device. Some SMDs are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, or vibration, making them suitable for industrial or outdoor applications.
- Cost: While high-performance SMD may be more expensive, ity can provide significant benefits in terms of reliability and efficiency. Evaluate the trade-offs between cost and performance to find the right balance for your project.
Challenges in Working with SMDs
Despite their many advantages, SMDs come with some challenges. Here are a few common issues when working with SMD:
- Soldering Difficulty: SMDs are small and require precision soldering techniques. While automated soldering is often used in manufacturing, manual soldering can be difficult and requires special skills and equipment.
- Repair Complexity: If an SMD becomes damaged, repairing it can be challenging. The small size of the components makes it difficult to replace or repair them without specialized tools.
- Thermal Sensitivity: SMDs are more sensitive to heat than traditional components. Careful temperature control is essential during the soldering and reflow process to avoid damaging the components.
FAQs: Everything You Need to Know About SMDs
Q: How do SMDs differ from traditional components?
A: SMDs are mounted directly on the surface of the PCB, while traditional components are inserted through holes in the board. This difference allows SMDs to be smaller and more compact.
Q: Can SMD be used in high-power applications?
A: While SMDs are typically used in low- to medium-power applications, high-power SMD is available with the right thermal management techniques to handle greater power demands.
Q: How does the SMT process improve manufacturing?
A: Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) improves manufacturing by allowing components to be placed more efficiently using automated machinery, reducing assembly time, and improving consistency.
Unlock the Power of SMDs: Boost Performance and Reduce Costs
Are you wondering, what does SMD mean and how can it benefit your next project? Surface-Mount Devices (SMDs) play a critical role in enhancing electronic designs. By utilizing SMDs, you can improve performance, reduce production costs, and streamline your design process. These compact components allow for more efficient use of space while maintaining high functionality. Whether you're developing consumer electronics or industrial systems, SMDs offer a reliable solution for improving device performance. Start exploring our wide selection of SMDs today and take your project to the next level!
© 2025 DXM Blog. All rights reserved.
Author: Ivan Huang
Recommended for you
What Is Positive Temperature Coefficient? Expert Guide on PTC Thermistors
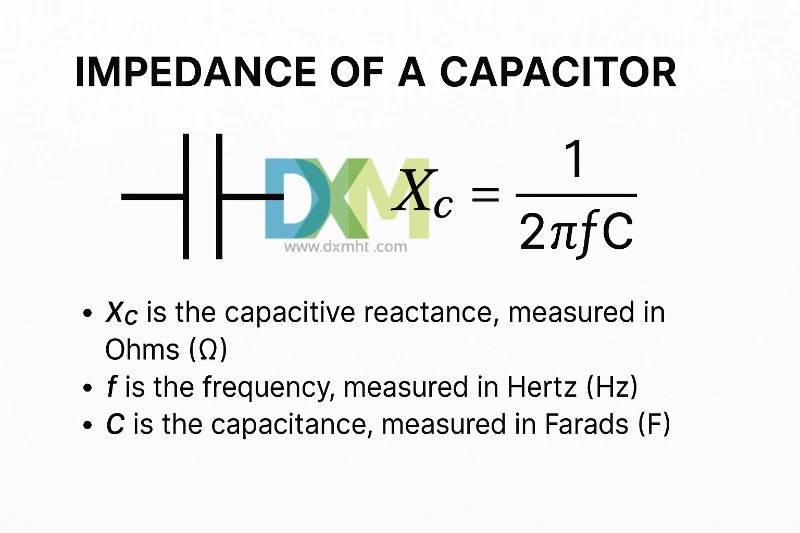
How to Find Impedance of a Capacitor: Guide for Professionals

how to calibrate rtd pt100?

Capacitor 104 Value: Essential Guide for Electronics Professionals

Positive Temperature Coefficient Heater: An Essential Guide of PTC Heater
What is an Electronic Ballast PTC Thermistor? Insights from DXM.
Logistics
Is your logistics and distribution service reliable?
Yes, we cooperate with a number of well-known logistics companies to ensure the timeliness and reliability of logistics and distribution services and provide you with a satisfactory distribution experience.
Shipment
1)Small order quantity and small packing:cargo may be arranged by courier;
2)Bulk order and big volume:shipment may be arranged by sea or by air as per customer’s requirements on FOB, C&F,CIF or LCL terms and do prompt shipment which is very important for our customers, so we do this matter seriously and we may arrange our shipment in time due to our rich experiences in this line. We may also accept the shipment on the term of freight prepaid or freight collect.
Can I change my shipping address?
Yes, you can contact our customer service team to modify the delivery address before order confirmation to ensure that the order can be accurately delivered to the address you specify.
Price and Payment
Do you offer bulk purchase discounts?
Yes, we offer bulk purchase discounts; the specific discount rate depends on the order quantity and cooperation method.
Are invoices provided?
Yes, we provide legal invoices that can be used for reimbursement and accounting records.
You may also like

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design

PTC Thermistors for Ballast Electronic and Energy Saving Lighting Intelligent Preheat Start MZ12 | DXM
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2025 DXM | All Rights Reserved.

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd