Understanding Thermistor: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn all about thermistors with DXM. This comprehensive guide explains what a thermistor is, its function, and its various applications. Understand the technology behind this temperature-sensitive resistor and how it benefits your projects. Discover the DXM difference in thermistor quality and reliability.
- What is a Thermistor?
- Types of Thermistors
- Applications of Thermistor
- How Does a Thermistor Work?
- How to Choose the Right Thermistor?
- Advantages of Using Thermistor
- Challenges and Limitations of Thermistor
- Q&A: Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a thermistor used for?
- How does a thermistor work?
- What are the main types of thermistors?
- How do I choose the right thermistor?
- Conclusion: The Importance of Thermistors in Modern Technology
What is a Thermistor?
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature. It is made from ceramic materials that exhibit a high sensitivity to temperature changes. Thermistors are used in a wide range of applications, such as temperature sensing, regulating, and overcurrent protection. If you’ve ever wondered what is a thermistor and why it’s used in electronics, this guide will answer all your questions.
Types of Thermistors
There are two primary types of thermistors: NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) and PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient).
- NTC Thermistors: The resistance of NTC thermistors decreases as the temperature increases. This type of thermistor is ideal for applications where the temperature is expected to rise gradually, such as temperature sensors in home appliances and automotive systems.
- PTC Thermistors: PTC thermistors, on the other hand, increase in resistance with temperature. They are commonly used in overcurrent protection and circuit-breaking devices due to their ability to limit current flow when the temperature becomes too high.
Applications of Thermistor
Thermistors play a crucial role in many different fields and are integral to the functionality of various devices and systems. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Temperature Sensors: NTC thermistors are often used in digital thermometers, thermostats, and HVAC systems to monitor temperature changes accurately.
- Overcurrent Protection: PTC thermistors are used to protect sensitive circuits by limiting the flow of current when the circuit becomes overloaded.
- Battery Management Systems: Thermistors help to ensure the safety and longevity of batteries by regulating their temperature, preventing overheating or damage.
- Automotive Systems: Thermistors are found in car engines, where they help monitor temperature and ensure that components are not subjected to damaging heat levels.
-
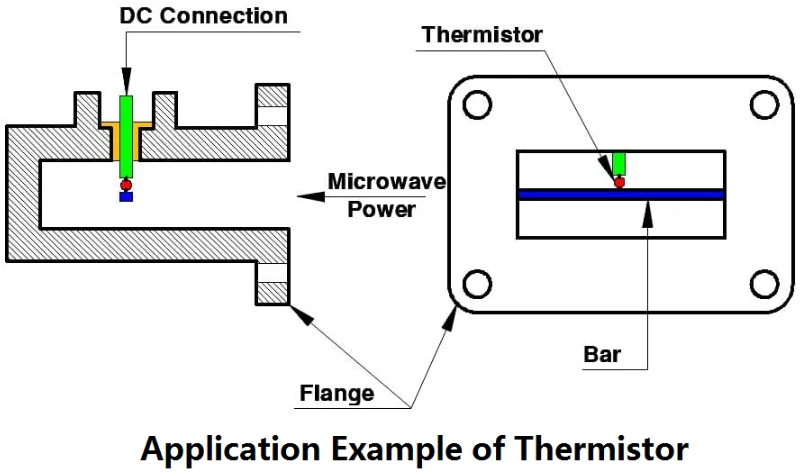
How Does a Thermistor Work?
Now that you understand what a thermistor is, it’s important to know how it functions. The key to a thermistor’s operation is its resistance, which varies with temperature. As the temperature changes, so does the resistance of the thermistor. The relationship between resistance and temperature is generally nonlinear, making thermistors more sensitive to temperature variations than standard resistors.
In practical applications, thermistors are often paired with microcontrollers or other circuitry that can measure the resistance and convert it into a temperature reading. This makes thermistors highly effective for precise temperature monitoring in various devices.
How to Choose the Right Thermistor?
Choosing the correct thermistor is critical to ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your temperature sensing system. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a thermistor:
- Temperature Range: It’s important to select a thermistor that can operate effectively within the temperature range of your application. For example, industrial applications may require thermistors that can withstand extreme temperatures, while consumer electronics may only need thermistors for more moderate temperature ranges.
- Resistance at Room Temperature: The resistance of the thermistor at a baseline temperature (usually 25°C) is a key specification to consider. The resistance value will influence how the thermistor behaves at higher or lower temperatures.
- Size and Form Factor: Depending on your space requirements, you may need a small thermistor or a surface-mount thermistor that fits within the design of your circuit board.
- Accuracy and Precision: Some thermistors offer higher accuracy and better temperature response than others, which is critical for applications where precise temperature measurement is necessary.
Advantages of Using Thermistor
Thermistors offer several benefits that make them highly useful in a wide range of applications:
- High Sensitivity: Thermistors exhibit a sharp, measurable change in resistance over a small temperature range, which allows for precise temperature sensing.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to other temperature sensors, thermistors are relatively inexpensive to produce, making them an economical choice for many applications.
- Small Size: Thermistors are compact and lightweight, allowing them to fit into small devices and circuits.
- Reliability: With proper handling, thermistors offer long-term reliability and can perform consistently over many years.
Challenges and Limitations of Thermistor
While thermistors offer many benefits, they also have some limitations that need to be considered:
- Nonlinear Response: Thermistors do not have a linear relationship between temperature and resistance, which can complicate temperature calculations in certain applications. However, this can be mitigated with the use of lookup tables or calibration techniques.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Thermistors can be sensitive to rapid changes in temperature, which may affect their accuracy in some environments.
- Long-Term Stability: While thermistors are generally reliable, prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures or excessive current may reduce their lifespan and affect performance.
Q&A: Frequently Asked Questions
What is a thermistor used for?
A thermistor is primarily used for temperature measurement and regulation in various applications, including consumer electronics, automotive systems, and medical devices.
How does a thermistor work?
A thermistor works by changing its resistance in response to temperature changes. This resistance change is then measured to determine the temperature accurately.
What are the main types of thermistors?
The two main types of thermistors are NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) and PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient). Each type has different applications based on how their resistance changes with temperature.
How do I choose the right thermistor?
When selecting a thermistor, consider the temperature range, resistance value, accuracy, and size to ensure it fits the requirements of your application.
Conclusion: The Importance of Thermistors in Modern Technology
In conclusion, a thermistor plays a crucial role in modern technology. Its ability to detect temperature changes with high accuracy makes it essential in various industries. Whether you're asking, "What is a thermistor?" or considering its application, the device's affordability and reliability are key benefits.
Thermistors are commonly used in electronics, automotive systems, and home appliances. Their resistance changes with temperature, providing precise readings for temperature control. This makes thermistors an excellent choice for engineers and product designers.
Understanding how thermistors work ensures better decision-making when selecting temperature sensors for your projects. By using thermistors, you can achieve accurate temperature monitoring at a low cost.
© 2025 DXM Blog. All rights reserved.
Author: Ivan Huang
Updated on 23th March 2025
Recommended for you

What Is Positive Temperature Coefficient? Expert Guide on PTC Thermistors

Unlocking the 103 Capacitor: An Essential Guide for Professionals

Where Can I Buy Resistors? Your Expert Sourcing Guide

How to Find Impedance of a Capacitor: Guide for Professionals

how to calibrate rtd pt100?

Capacitor 104 Value: Essential Guide for Electronics Professionals
Price and Payment
Do you offer bulk purchase discounts?
Yes, we offer bulk purchase discounts; the specific discount rate depends on the order quantity and cooperation method.
Are invoices provided?
Yes, we provide legal invoices that can be used for reimbursement and accounting records.
Customized Services
Free sample availability
You can contact our representative via email, fax or phone to specify the sample you need and provide your courier's account number (such as UPS, FedEx, DHL, TNT, etc.).. And we’ll send you samples free of charge through your courier by freight collection.
Custom-made sample/order
SHENZHEN DXM TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. are structured by high-tech talents from famous university
in China and accompanied with a batch of ceramic-sensitive components experts and technology
specialist, have powerful R&D and technology capabilities.DXM is one of a few manufacturers
master core production technology of ceramic-sensitive components in the world.
Samples and orders can be custom-made per customer’s requirements, as below:
1. Application environment of product
2. Required specifications or technical parameters
3. Reference sample
4. Reference drawing
Logistics
Does it support express delivery?
Yes, we support express delivery services. You can choose different delivery methods according to your needs, including ordinary express delivery and expedited express delivery.
You may also like

PT1000 Temperature Sensor: DXM Precision Platinum RTD Solutions

KTY83-110 Sensor with Silicon Glass Thermistor

Bracket Type NTC Thermal Sensor MF52X for Precise Temperature Measurement

Glass Thermistors MF58E for High-Precision Applications

High Precise NTC Sensors for Temperature Measurement and Control

WMZ12A 75S PTC Thermistors for Over-Current and Over-Load Protection

SMD Sensors: Advanced Temperature Sensing Excellence

Thermistor PTC MZ11 Series for Light Efficient Design
Get in Touch
Discover premium thermistors, sensors, and resistors tailored to your needs.Our dedicated team of experts is available to assist with product selection, technical queries, and after-sales service. Contact us for custom solutions and experience exceptional customer support.
© 2025 DXM | All Rights Reserved.

 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Whatsapp: +8618927361658
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd.
DXM PTCNTC
Shenzhen DXM Technology Co., Ltd